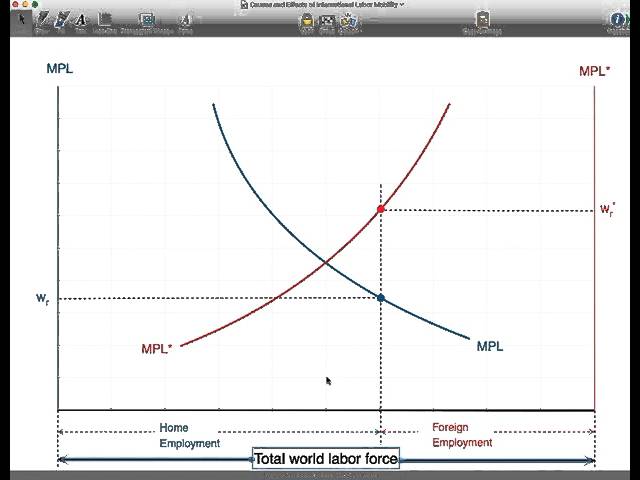
Pinned Items
-
Stream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
-
Stream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
-
Stream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
Recent Activities
-
Post is under moderationStream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
-
Post is under moderationStream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
-
Post is under moderationStream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
-
Post is under moderationStream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
-
Stream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
-
Stream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
-
Stream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
-
Post is under moderationStream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
-
Post is under moderationStream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
-
Stream item published successfully. Item will now be visible on your stream.
There are no activities here yet